Blockchain Technology
History of Blockchain:
First and foremost, let us go through some facts and stats that
the web has to offer us regarding the emergence of Blockchain.
· The first decentralized blockchain
was conceptualized by a person (or group of people) known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Thus, blockchain got its first real-world application with the launch of
Bitcoin in January 2009.
· Moreover, Cryptographer David Chaum is said to be the first one to propose a
blockchain-like protocol in his 1982 dissertation "Computer Systems
Established, Maintained, and Trusted by Mutually Suspicious Groups. Later in the late 1990s, Cypherpunk Nick Szabo proposed using a blockchain how to
secure a digital payments system, known as bit gold (which was never implemented).
· Blockchain as
technology was first outlined in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta,
two mathematicians who wanted to implement a system where document time stamps
could not be interfered with.
What is
Blockchain?
The standard definition of blockchain reads that A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and oftentimes public, digital
ledger consisting of records called blocks that are used to
record transactions across many computers so that any involved block cannot be
altered retroactively, without the alteration of all subsequent blocks. This
allows the participants to verify and audit transactions independently and
relatively inexpensively. A blockchain database is managed autonomously using
a peer-to-peer network and a distributed timestamping server.
Thus,
Blockchain
is a type of shared database that differs from a traditional database in the
way how it stores information; blockchains store data in blocks which are then
linked together via cryptography. When new data arrives, it is entered into a new
block and when the block is filled with data, it is chained on top of the
previous block, causing the data to be chained together in chronological order.
Why? and What do you need
to know about Blockchain?
1.
Blockchain technology
is broader than finance. It can be applied to any multi-step transaction that requires
traceability and visibility. Supply chain is a notable use case where
blockchain can be leveraged for the management and contracting as well as audit
of the origin of products. It could also be leveraged
for votation platforms, securities, titles, and document
management - amongst many other uses. As the digital and physical worlds
converge, the practical applications of Blockchain will only grow.
2.
Blockchain
technology doesn't have to exist publicly. It can also exist
privately - where nodes are simply points in a private network
and the Blockchain acts same as a distributed ledger. Financial institutions
specifically are under tremendous pressure to demonstrate regulatory compliance
thus many of them are now moving ahead with Blockchain implementations. Secure
solutions like Blockchain can be a crucial building block to reduce compliance
costs.
3.
The exponential and
disruptive growth of Blockchain will come from the convergence of
public and private Blockchains to an ecosystem where firms, businesses, customers,
and suppliers can collaborate in a secure, auditable, and virtual way.
4.
Various types of information can be stored on a blockchain,
but the most common use by far is as a ledger for transactions. Decentralized blockchains
are immutable, which means imported data is immutable. For Bitcoin, this means
that transactions are permanently recorded and can be viewed by everyone.
Blockchain is the
technology behind cryptocurrency – for instance the Bitcoin currency, but
Bitcoin is not the only version of the blockchain distributed ledger system on
the market. There are several other cryptocurrencies that have their own
blockchain and distributed ledger architectures. Meanwhile, the
decentralization of the technology has also led to some schism or division in
the Bitcoin network, creating forks of the ledger where some miners use a
blockchain with one set of rules, and others use a blockchain with another set
of rules.
The
key thing to understand here is that Bitcoin merely uses blockchain to
transparently record a ledger of payments, but blockchain can, in theory, be
used to immutably record any number of data points. As mentioned above in the
reasons, this could be in the form of transactions, votes in an election,
product inventories, state identifications, deeds to homes, and much
more.
Blockchain from an Engineer’s Point of View:
Perhaps
most centrally, the blockchain is an information technology. But the blockchain
technology is also many other things. The blockchain as decentralization is a
revolutionary new computing paradigm. The blockchain is the embedded economic
layer the Web never had. The blockchain is the coordination mechanism, the
line-item attribution, credit, proof, and compensation rewards tracking scheme
to encourage participation by any intelligent agent in any collaboration. The
blockchain “is a decentralized trust network.” The blockchain is Hayek’s
multiplicity of private complementary currencies for which there could be as
many currencies as Twitter handles and blogs, all fully useful and accepted in
their own hyperlocal contexts. The blockchain is a cloud venue for
transnational organizations. The blockchain is a means of offering personalized
decentralized governance services, sponsoring literacy, and facilitating
economic development. The blockchain is a tool that could prove the existence
and exact contents of any document or other digital asset at a particular time.
The blockchain is the integration and automation of human/ machine interaction
and the machine-to-machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) payment network
for the machine economy. The blockchain and cryptocurrency is a payment
mechanism and accounting system enabler for M2M communication. The blockchain
is a worldwide decentralized public ledger for the registration,
acknowledgment, and transfer of all assets and societal interactions, a
society’s public records bank, an organizing mechanism to facilitate
large-scale human progress in previously unimagined ways. The blockchain is the
technology and the system that could enable the global-scale coordination of
seven billion intelligent agents. The blockchain is a consensus model at scale,
and possibly the mechanism we have been waiting for that could help to usher in
an era of friendly machine intelligence.
To Conclude-Blockchain as one of history’s prominent technological
inventions:
Speculatively
looking towards the longer run, there might be a large possibility space of
intelligence that includes humans, enhanced humans, different forms of human/
machine hybrids, digital mind file uploads, and different forms of artificial
intelligence like simulated brains and advanced machine learning algorithms.
The blockchain as an information technology might be able to ease the future
transition into a world with multiple kinds of machine, human, and hybrid
intelligence. These intelligences would likely not be operating in isolation
but would be connected to communications networks. To achieve their goals,
digital intelligences will want to conduct certain transactions over the
network, many of which could be managed by blockchain and other consensus
mechanisms.
Credits and References: Prathmesh Brahmankar(TY Metallurgy, Team Tech Tuesday)
1. A book by Melanie Swan titled Blockchain: Blueprint For a New Economy.
2. Investopedia articles for Facts, Figures and Definitions. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp
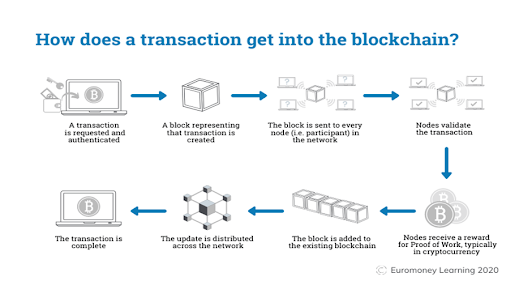
3. https://www.euromoney.com/learning/blockchain-explained/how-transactions-get-into-the-blockchain
4. Euromoney.com
NOTE:-
This blog is meant for Educational Purpose only .We do not own any Copyrights related to images and information , all the rights goes to their respective owners . The sole purpose of this blog is to Educate, Inspire, Empower and to create awareness in the viewers. The usage is non-commercial(Not For Profit) and we do not make any money from it.
FOLLOW US ON:-
INSTAGRAM :
LINKEDIN:
YOUTUBE:-

Comments
Post a Comment